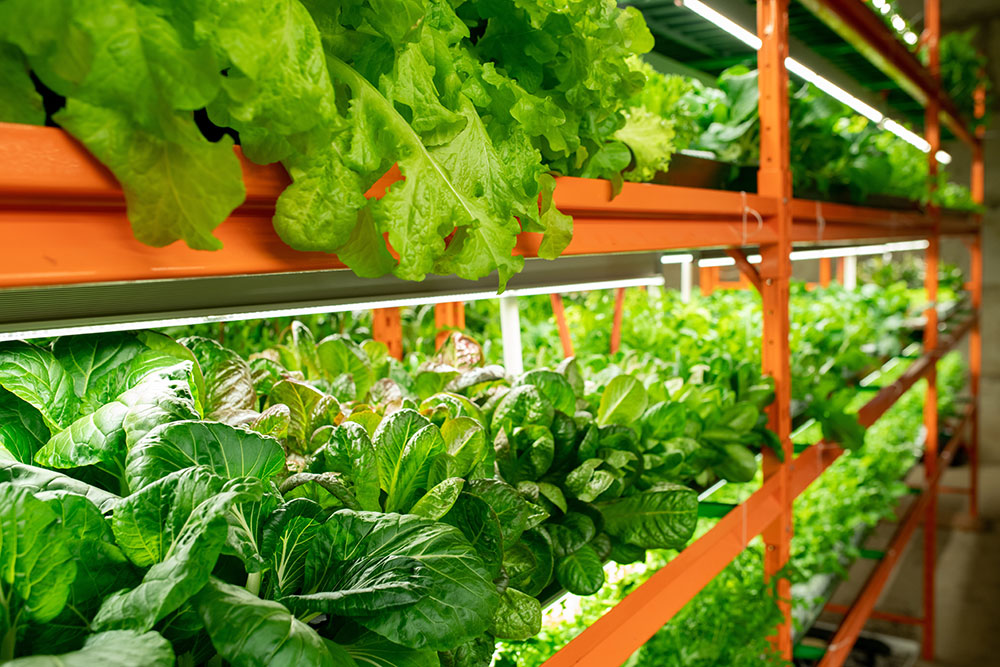
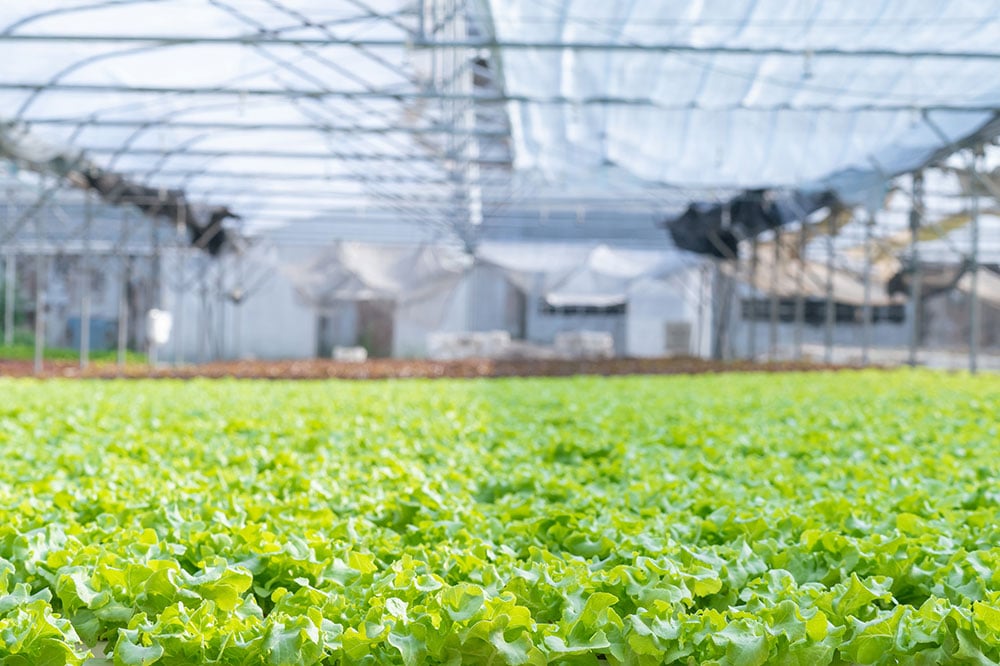
Imagine a farm not spread out over sprawling fields, but soaring upwards, layer upon layer, right in the heart of a bustling city. This is the essence of vertical farming, a groundbreaking approach to agriculture that's changing how we grow our food. At its core, vertical farming is about cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers in controlled environments. It leverages soilless farming techniques such as hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics to create a fusion of traditional agricultural wisdom with cutting-edge technology.
THE ADVANTAGES OF VERTICAL FARMING
The benefits of vertical farming are manifold. Environmentally, vertical farming requires less land which means less deforestation and habitat loss. Meeting the land requirements for traditional farming requires growing food away from the population centers where the food is consumed. Not only does this require increased effort and equipment to transport the food, but it is estimated that 14% of food is lost between harvest and retail. By bringing farms to urban areas, vertical farming slashes transportation emissions and costs and reduces the time from harvest to consumption, to ensure fresher produce.
Efficiency is another hallmark of vertical farms. These farms operate year-round to produce consistent yields irrespective of seasonal changes. While traditional farms must adhere to growing seasons, vertical farms can harvest on a perpetual cycle.
Vertical farms are also prime examples of water and energy conservation. They use sophisticated systems that minimize waste and maximize sustainability. By controlling the environment, vertical farms are not subject to the randomness of variables like weather, pests, and time of the year that traditional farms must contend with.
TYPES AND METHODS OF VERTICAL FARMING
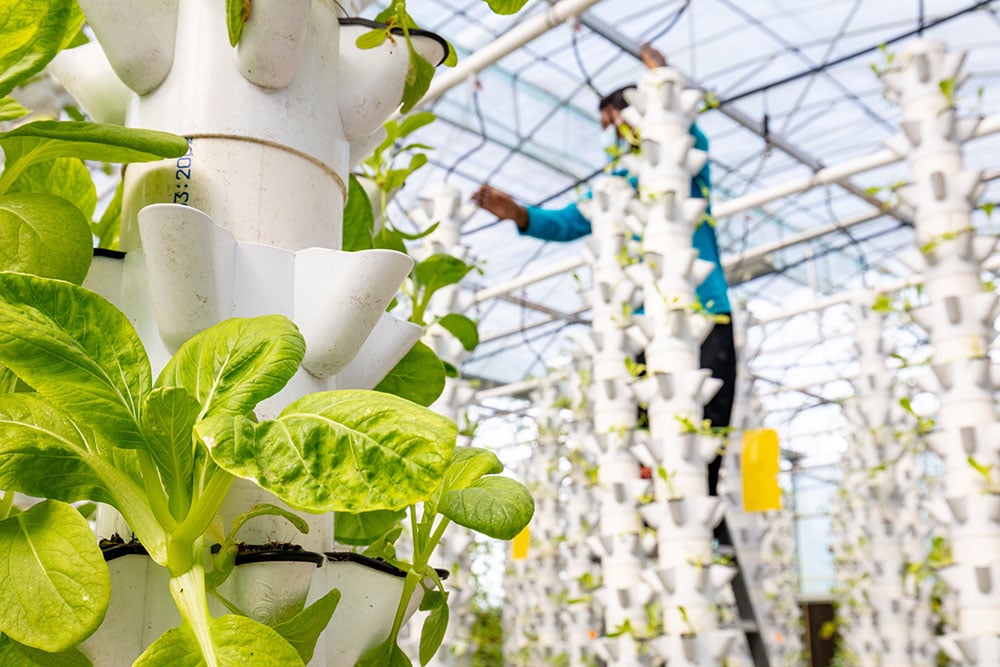

The world of vertical farming is diverse and it includes a variety of methods and environments. Indoor vertical farms, for instance, often repurpose buildings like warehouses by using artificial lighting and climate controls to create perfect growing conditions. Outdoor vertical farms make use of natural sunlight by stacking plant containers to save space. The hanging gardens of Babylon are a great example of ancient vertical farming techniques and showcase just how long these techniques have been used.
Vertical farms can also use the sunlight and optimal growing conditions to their benefit when available. Vertical greenhouses blend traditional greenhouse practices with vertical techniques to provide the best of both worlds. The vertical greenhouses can use filtered outdoor air and sunlight to boost plant performance while also supplementing these conditions when the outdoor conditions are not quite right. Not to be overlooked are vertical gardens, which can range from small home setups for herbs and small vegetables to extensive urban installations. With a vertical setup, even patios and balconies can produce a great deal of food.
HOW DOES VERTICAL FARMING WORK?
The magic of vertical farming lies in its ingenious use of space and resources. Central to its success is the use of LED lighting, which provides plants with the ideal light spectrum while being energy-efficient. These farms typically forgo soil, and instead use hydroponic or aeroponic systems where water and nutrients are delivered directly to the roots.
This approach not only reduces water usage, it also accelerates plant growth. These systems are finely tuned to control every aspect of the environment, from humidity to temperature to ensure optimal growing conditions for a variety of crops. Using advanced control systems, the water delivered to the plants can be optimized for proper pH and nutrient profiles while the air delivered to the plants can maintain the proper microclimate around each plant. Vertical farming provides an entire world of optimization that is simply not possible in a traditional farming setup.
PLANTS SUITABLE FOR VERTICAL FARMING
Vertical farming isn’t suitable for every type of crop. It excels with plants like leafy greens. Lettuce, spinach, and kale as well as a variety of herbs all grow very well in vertical farm setups. These plants thrive under the controlled conditions of vertical farms. Even small fruits like strawberries and grains like rice and other vegetables can be successfully cultivated. What’s important is matching the crop to the specific conditions and technologies of the vertical farming setup. Research is continually expanding the selection of crops that can be successfully cultivated in a vertical farming setup.
TECHNOLOGIES DRIVING VERTICAL FARMING
The advancement of vertical farming is tightly linked to technological innovation. Advanced control systems have revolutionized how water and nutrients are delivered to plants. Automation also plays a key role by reducing labour costs and improving precision in tasks like watering and harvesting. As technology evolves, so too does the efficiency and scope of what can be achieved in vertical farming.
Equally important is how water and grow environments are managed. As a key component of food supply chains, safety and cleanliness are paramount. Systems like the FoodSafe Slot Drain help ensure that liquid water is properly managed and removed quickly so that high-humidity environments do not occur. Vertical farms can be cleaned quickly and easily without the wastewater disturbing the plants.
When liquid water is not handled properly, microbial and mold growth can become an issue and plant transpiration is slowed down. Maintaining proper vapor pressure differential in a plant’s canopy requires a grow environment that can control the air and water conditions in the vertical farm. FoodSafe Slot Drains takes the complexity out of wastewater management for vertical farms.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT VERTICAL FARMING
Vertical farming is a fascinating topic with no shortage of questions to answer.
What is indoor vertical farming?
It's a method of growing crops in controlled indoor environments that uses layers and advanced farming techniques.
How does vertical farming conserve resources?
By recirculating water and optimizing space, it significantly reduces resource usage. Controlling the grow environment means controlling the energy and water resources that are input to or taken out of the system.
What are the challenges of vertical farming?
The main challenges include high initial costs and energy requirements, particularly for lighting and climate control. The challenges are being offset by rapid innovation in these areas.
Can vertical farming be implemented at home?
Absolutely! Home-based vertical gardens and DIY hydroponic systems are becoming increasingly popular.
What is the future of vertical farming?
The future looks bright, with vertical farming poised to make urban, sustainable farming more prevalent.
How is vertical farming different from traditional farming?
It uses vertical space and controlled environments which differ significantly from traditional field farming.
What are the costs involved in setting up a vertical farm?
While variable, the costs can be substantial, especially for high-tech setups.
VERTICAL FARMING - THE FUTURE OF AGRICULTURE
Vertical farming is more than just an agricultural method; it's a vision for a sustainable, efficient future in food production. Its benefits, from environmental conservation to urban adaptability, position it as a powerful solution to modern agricultural challenges.
As technologies advance and become more accessible, vertical farming is set to play a crucial role in our global food system by offering a fresh approach to bringing food from farm to table.


